Flurbiprofen vs Ibuprofen
Introduction
For patients looking to alleviate symptoms such as pain, inflammation, and fever, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often the preferred solution. Through the inhibition of the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX), and the subsequent conversion of arachidonic acid into thromboxanes, prostaglandins, and prostacyclins, NSAIDs can act as effective anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, and analgesic agents.
Different classifications of NSAIDs typically depend on the drug’s chemical structure. While Ibuprofen and Flurbiprofen treat the same symptoms, the chemical composition differs. Both Flurbiprofen and Ibuprofen are propionic acid derivatives. However, the difference is categorized by the substitution of the benzene ring. While Flurbiprofen contains a fluorine atom on this ring, Ibuprofen has an isobutyl group. This composition has implications in treatment plans whereby different NSAIDs are prescribed to patients depending on their health, weight, history of the disease, and any other medications they take that might interfere with the NSAID.
About Flurbiprofen and Ibuprofen
What is Flurbiprofen?
Flurbiprofen is often used by patients with chronic pain, inflammation, or related symptoms. First derived from propionic acid in the 1960s by the company Boots Group PLC, Flurbiprofen was usually the subject of research by doctors searching for an effective analgesic and anti-inflammatory agent. Researchers discovered that it was particularly efficient at inhibiting the production of chemicals like prostaglandins that contributed to pain, inflammation, and fever. Being a non-selective COX inhibitor, it could inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, which could decrease pain, inflammation, and fever quickly and effectively. Flurbiprofen was soon patented and introduced to the market as a prescription for pain and inflammation, mostly for rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis at first. Over time, it proved effective for menstrual cramps, dental pain, musculoskeletal injuries, and post-operative pain. Today, Flurbiprofen is widely used under the brand names “Ansaid,” “Ocufen,” and “Froben,” among many others.
What Conditions Is Flurbiprofen Approved To Treat?
Flurbiprofen is approved for the treatment of various ailments that produce symptoms of pain, inflammation, and/or fever, along with others;
- Arthritis: Flurbiprofen is approved for the treatment of various types of arthritis, which includes rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. These are commonly associated with inflammation or breakdown of the joints or cartilage.
- Menstrual Pain: Flurbiprofen can also be used to relieve pain and menstrual cramps experienced during the menstrual cycle.
- Eye Conditions: Flurbiprofen eye drops are approved for treating inflammation and pain caused by cataract surgery.
- Dental Pain: Flurbiprofen is often prescribed after a tooth extraction or to relieve a toothache.
- Post-operative Pain: Flurbiprofen is often recommended to alleviate pain following surgery.
Note that Flurbiprofen is usually prescribed in combination with other treatment plans and can only act as an anti-inflammatory or pain relief agent. Further treatment depends on other medications, procedures, and treatment plans.
How Does Flurbiprofen Work for Arthritis?
A diagnosis of various types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, usually involves an inflammation of the joints. NSAIDs focus on inhibiting COX-1 and COX-2, the enzymes that are induced during inflammatory responses, to reduce the production of prostaglandins. This could result in reduced inflammation and pain. Flurbiprofen can help patients manage the symptoms of arthritis by increasing mobility which is achieved by significantly lesser swelling and joint pain. Movement could significantly improve the quality of life of most patients. In some cases, Flurbiprofen could prove more effective due to its inhibition of the COX enzymes. This characteristic might lead to a longer duration of pain relief in some use cases. However, response to medication may differ from individual to individual, and while some may experience a noticeable difference, others might respond better to another type of NSAID.
What is Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is also a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), highly effective for the treatment of pain, fever, and inflammation. First discovered by Steward Adams and John Nicholson in 1961, Ibuprofen was initially called Brufen. More than a decade later, in 1974, Ibuprofen was released to the United States market. Ibuprofen is primarily useful for fever, pain, and inflammation associated with different kinds of diseases. The existence of a variety of NSAIDs, including Ibuprofen, is beneficial for patients who might not respond to all NSAIDs.
Today, Ibuprofen is available all around the world, usually sold as an over-the-counter pain relief medication (under FDA dosage limits). It has been sold under the names Motrin and Advil since it was first released in the United States.
What Conditions Is Ibuprofen Approved to Treat?
Ibuprofen is approved to treat;
- Fever symptoms
- Mild to moderate pain caused by musculoskeletal conditions, dental issues, headaches, menstrual cycles, and more
- Inflammation caused by different types of arthritis
- Injuries, including soft tissues injuries that may lead to inflammation and pain
How Does Ibuprofen Work for Arthritis?
Subtle differences do exist between various NSAIDs, which may affect their potency and duration of relief. For Ibuprofen, achieving arthritic pain relief involves the same mechanisms, including inhibiting COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes to reduce inflammatory prostaglandins in the system. However, Ibuprofen has a lower affinity for the COX enzyme. Although it inhibits both enzymes, it is less selective when it comes to COX-1. This may lead to certain side effects, such as stomach irritation in some rare cases. Ibuprofen is often prescribed due to its availability and cost-effectiveness. Although it may be associated with certain side effects, it is much more extensively studied. This has allowed it to establish trust among patients. Moreover, individual factors may cause Ibuprofen to be more effective for certain patients when compared to others.
Effectiveness
How Effective Are Flurbiprofen and Ibuprofen for Treating Arthritis?
A study published by H.R. Mena in 1977 on treating arthritis with Flurbiprofen or Ibuprofen found no remarkable differences between the two. A dosage of 2400 mg Ibuprofen per day was compared to administering 120 mg Flurbiprofen per day in 15 clinics with five to eighteen patients per investigator, all suffering from definite or classical rheumatoid arthritis. Both drugs were effective in controlling rheumatoid arthritis symptoms to some extent. There were noticeable differences in fatigue, swollen joints, and grip strengths before and after administering the drugs. Moreover, side effects were also low with both drugs. In contrast, further research conducted in the following decades was reflected in a study published in the International Journal of Clinical Practice. This highlighted Flurbiprofen as a valuable alternative in treating rheumatoid arthritis due to its higher efficacy, tolerance, and duration of relief.
Another study on the efficacy of an S-flurbiprofen plaster for knee osteoarthritis, published in 2017, noted significant improvement in movement and a noticeable reduction in pain with lesser gastrointestinal side effects. Moreover, when given orally, Flurbiprofen has a lower incidence of gastrointestinal side effects when compared to other NSAIDs because of faster absorption and low dosage requirements. However, Ibuprofen is much more favorable for consumption in higher doses and is preferred by patients with gastrointestinal issues. For doctors, treatment plans usually depend on a patient’s medical history, adverse reactions to drugs, and other medications that may interfere with the drug. The efficacy and reaction of Flurbiprofen and Ibuprofen may vary from patient to patient.
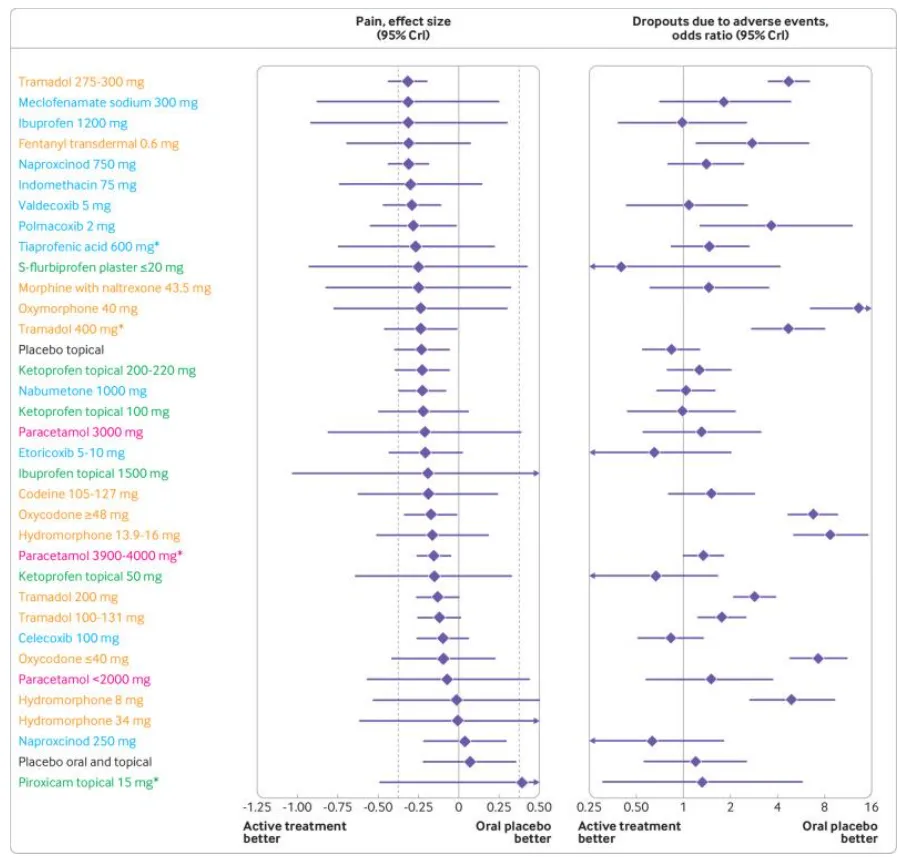
The figure above, presented in a meta-analysis of NSAIDs, ranked the S-flurbiprofen plaster and Ibuprofen higher than at least 25 other drugs. Moreover, the S-flurbiprofen plaster wasn’t far behind Ibuprofen in its effectiveness. In fact, the results of both NSAIDs were more or less similar. The active treatment yielded better results when it came to pain, which meant that the NSAIDs were more effective than placebos in treating pain from arthritis. However, Ibuprofen proved to be more effective. On the other hand, Ibuprofen had more dropouts than the alternative.
Dosage information
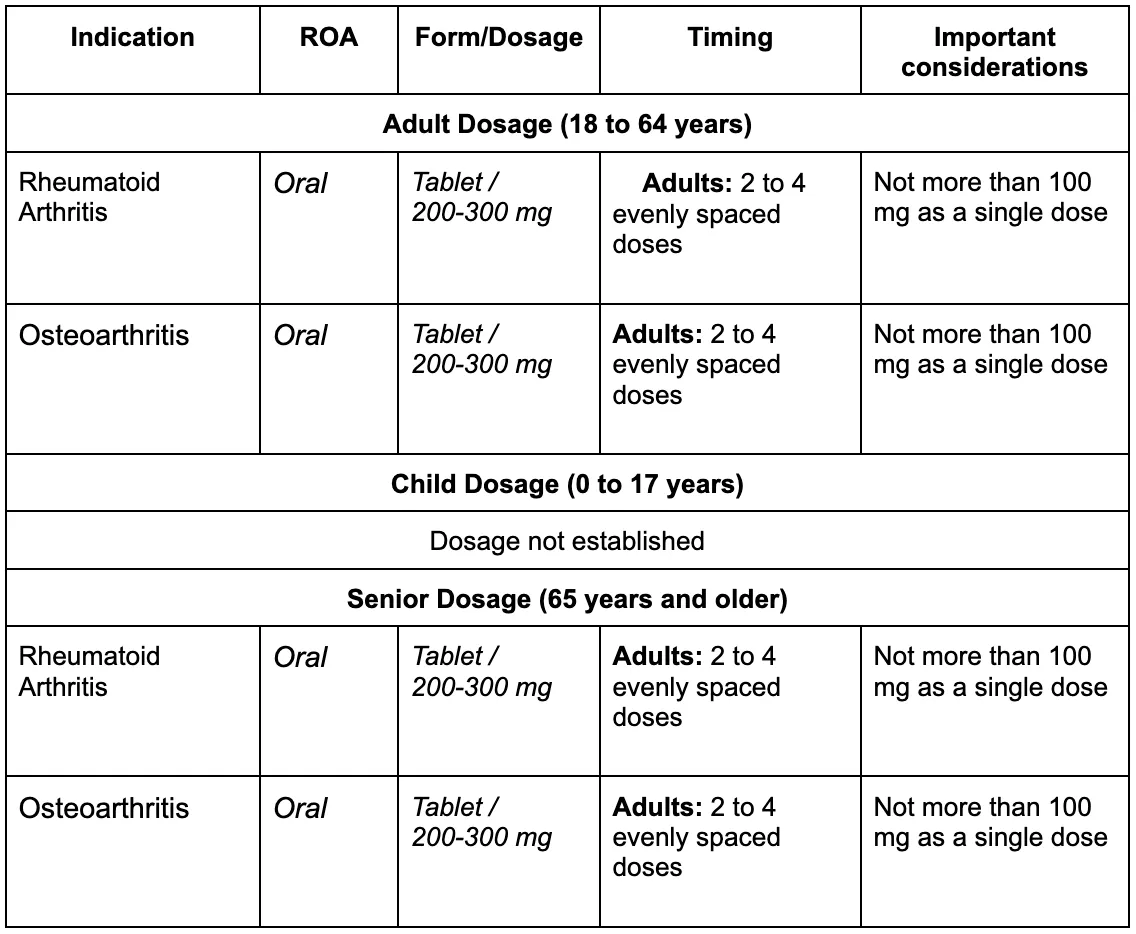
How is Flurbiprofen Administered for Arthritis?
Flurbiprofen Dosage Information
The oral dosage of Flurbiprofen for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis ranges from 200 mg to 300 mg per day in 2-4 divided doses with a maximum single dose of 100 mg. However, this may differ between individuals and can also be reduced over time to the lowest possible dose and the shortest possible duration to avoid side effects. However, patients with advanced renal disease or abnormal liver findings might require an adjustment or an alternate drug. Doses might need adjustment before they are prescribed to elderly patients.
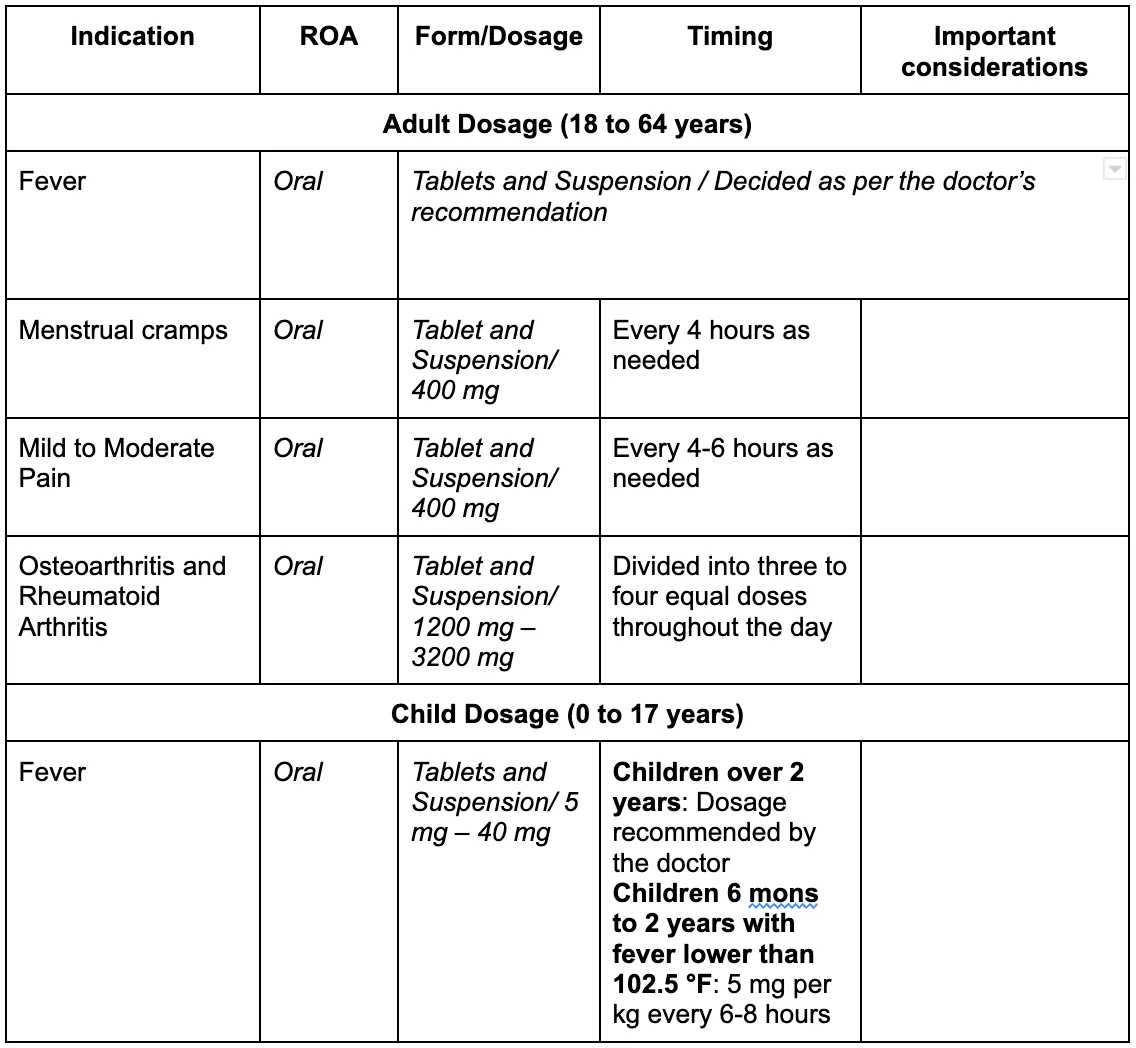
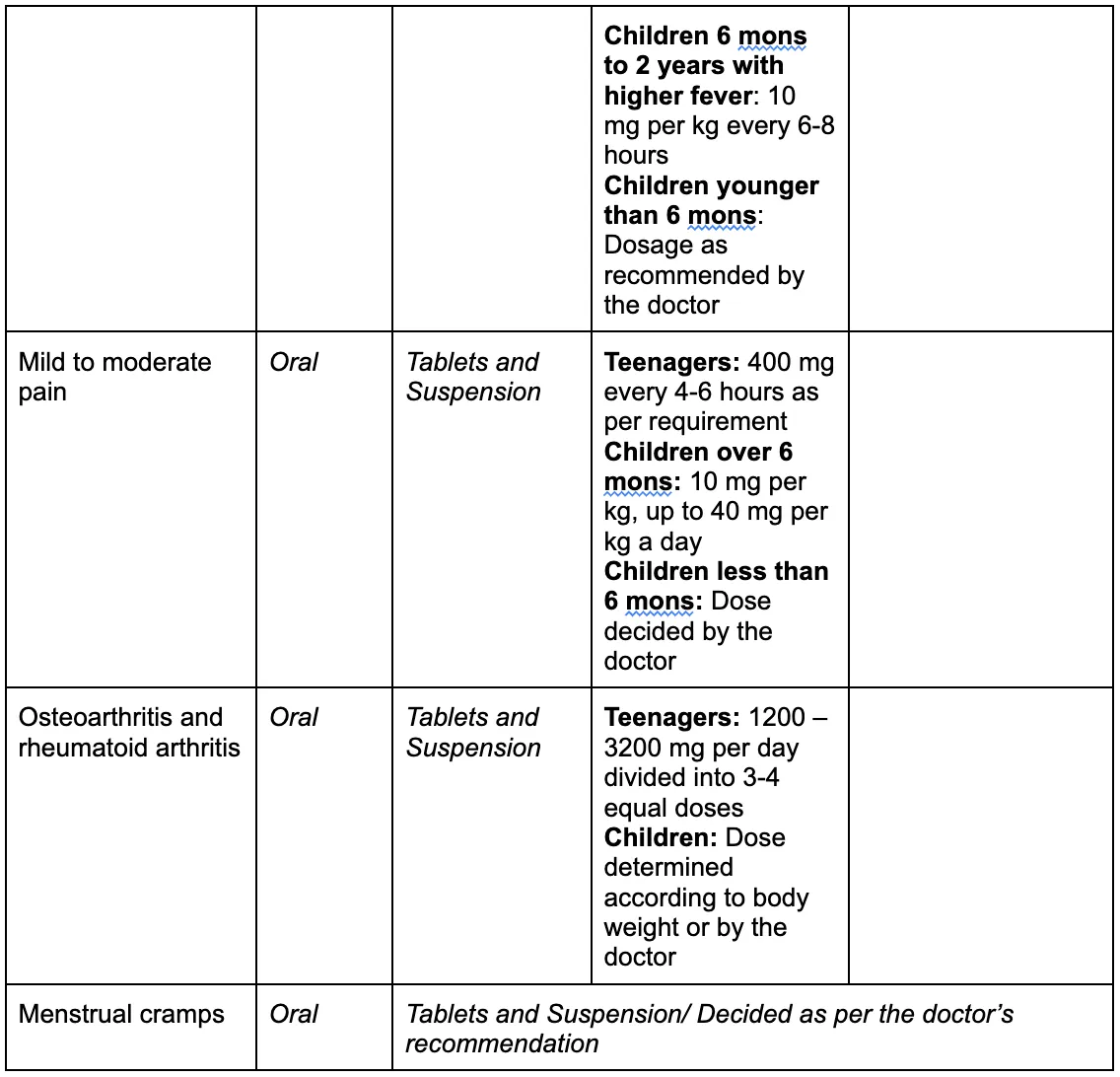
How is Ibuprofen Administered for Arthritis?
Ibuprofen dosage information
Ibuprofen is generally used to treat fever, pain, or inflammation as a result of multiple conditions. It can be used by children 6 months and older, adults, and the elderly. However, it is important to request your doctor for an altered dosage if you have ever had heart disease, blood pressure concerns, cholesterol issues, a history of stroke or blood clots, stomach ulcers or bleeding, liver disease, asthma, kidney disease, or other conditions. If you are pregnant, it is important to ask your doctor for advice before using the medication. Overdosing on Ibuprofen can lead to permanent damage to the stomach or intestines.
Side Effects
Understand that the following list does not include all possible side effects of the medication. Keep in mind that each medication may react differently for an individual based on their anatomy, health, medical history, and any medication they are currently taking. Make sure you read the package inserts and always inform your doctor regarding any possible medication or medical history so that you are well informed of the possible side effects.
What Are the Most-Common Side Effects of Flurbiprofen?
- Abdominal pain
- Indigestion
- Heartburn
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Stomach ulcers
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Skin allergies
- Swelling
- Sudden weight gain
- High blood pressure
- Kidney dysfunction (increased urination)
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Changes in vision
- Shortness of breath
Are There Any Potential Serious Side Effects of Flurbiprofen?
* If you experience any of these serious side effects, seek medical help immediately
- Chest pain that extends to the arms, jaw, back, or neck
- Trouble breathing and slurred speech
- Dark urine or pale stools, lack of appetite, pain in the upper abdomen, yellow skin or eyes, vomiting, nausea (these may indicate issues with the liver)
- Bloody urine, breathing problems, feeling faint, increased thirst, lack of appetite, nausea, swelling
- Black stool, black vomit, severe stomach pain, swelling, unusual bleeding, and bruising
- Signs of anaphylaxis such as gasping for breath, irregular or fasting breathing, fainting, pale skin, swollen eyes or eyelids, hives on the skin
Flurbiprofen is not recommended for women who are currently pregnant. If you have become pregnant while using this medication, inform your doctor immediately.
What Are the Most-Common Side Effects of Ibuprofen?
- Constipation
- Gas
- Feeling faint
- Bloating
- Anxiety
- Ringing ears
- Abdominal pain
- Indigestion
- Constipation
- Stomach ulcers
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
- Heartburn
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Skin allergies
- Swelling
Are there any potentially serious side effects of Ibuprofen?
* If you experience any of these serious side effects, seek medical help immediately
- Shortness of breath or extreme difficulty in breathing
- Sudden weight gain
- Swelling
- Peeling skin, fever, rash
- Hives, swelling of face, throat
- Fatigue
- Lack of appetite
- Yellowing skin and eyes
- Faster heartbeat
- Bloody urine
- Blurred vision or other issues with sight
- Headache, fever, and stiff neck
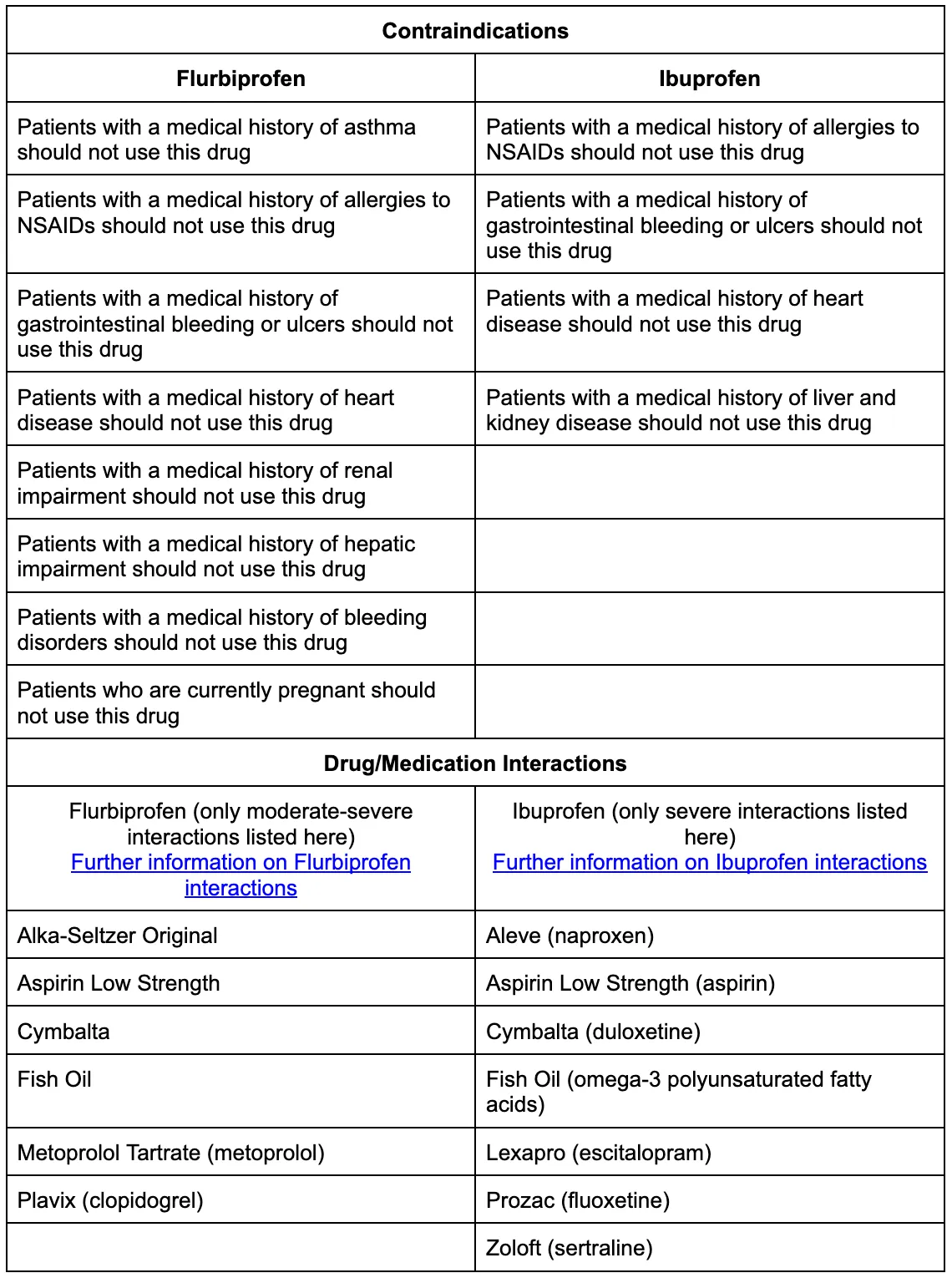
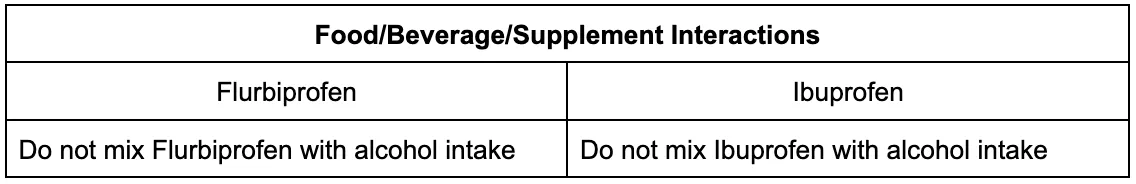
Contraindications and interactions
Warnings and general precautions for Flurbiprofen and Ibuprofen
Both Flurbiprofen and Ibuprofen can have significant effects on kidney and liver function, which is why it is essential that you avoid usage if you have pre-existing problems with liver and kidney functionality. NSAIDs can cause kidney damage in case of pre-existing issues and can quickly lead to dehydration. Moreover, it is important to avoid taking these medications during pregnancy, especially during the third trimester or breastfeeding. Remember to consult a medical professional before usage.
Any history of asthma, lung disease, breathing issues, or any cardiovascular risks must be discussed with your doctor. Your doctor may advise you to take lower dosages if you have a history of cardiovascular diseases. The same applies to gastrointestinal concerns, whereby people with a prior medical history of stomach ulcers and bleeding may be required to make dietary changes when consuming this medication.
Contraindications and important interactions for Flurbiprofen and Ibuprofen
Cost Comparison
How much do Flurbiprofen and Ibuprofen cost?
Flurbiprofen may cost up to $18.02 for 15 tablets of 100 mg each at a price of $1.20 per unit. For an adult consuming 300 mg a day, this may amount to approximately $108 per month. On the other hand, Ibuprofen can cost $10.74 for 6 tablets of 800 mg each with a price of $1.79 per unit. This amounts to $80.55 approximately for an adult consuming 1200 mg of Ibuprofen per day for a month.
Popularity of Flurbiprofen and Ibuprofen
The estimated number of prescriptions provided in the United States for Flurbiprofen in 2020 was 230,134. On the other hand, Ibuprofen prescriptions in the same year amounted to 16,533,209, reflecting much greater popularity for this drug.
There were also an estimated 21,628 patients in the United States who were using Flurbiprofen in 2020. On the other hand, 8,896,328 patients used Ibuprofen in the same year. This is a result of the studies and clinical trials associated with Ibuprofen, along with the fact that Flurbiprofen is a relatively newer drug. This is also reflected in the rankings; Ibuprofen ranks at 38, whereas Flurbiprofen ranks at 405 in the list of top drugs in the United States.
Conclusion
Takeaway
Flurbiprofen and Ibuprofen have established their efficacy and efficiency over time, whether through drug trials or patient reviews and treatments. The results aren’t just backed by clinical studies but also patient accounts which have established the fact that NSAIDs are a great course of treatment for chronic pain in most arthritis cases. In some cases, side effects might exist. However, with proper dosage monitoring and consultations with a physician, side effects can be avoided.
Both drugs might achieve the same results. However, they achieve them through different routes. Due to the difference in their composition, they may achieve better results with one patient and might not be as effective with another. It is essential to recognize medical histories, health, and individual patient characteristics before deciding upon a course of treatment.
Note that side effects and drug interactions, along with other considerations, are quite similar when it comes to both NSAIDs. However, it is essential to consult a medical professional and ask relevant questions to know more about the drugs and how they may interact.