Coreg vs Carvedilol
Introduction
Coreg and Carvedilol are medications commonly used in the treatment of cardiovascular conditions. While Coreg is a brand-name medication, Carvedilol is available as a generic version. Both medications have been proven effective in managing conditions such as heart failure and hypertension.
About Coreg and Carvedilol
What is Coreg
Coreg, also known by its generic name Carvedilol, is a medication used for the treatment of various cardiovascular conditions. It belongs to a class of drugs called beta-blockers.
Coreg works by blocking certain receptors in the body, specifically beta-adrenergic receptors. By doing so, it reduces the effects of stress hormones like adrenaline on the heart and blood vessels, resulting in decreased heart rate, lowered blood pressure, and improved heart function.
What conditions is Coreg approved to treat?
Coreg is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat the following conditions:
- Heart Failure: Coreg is indicated for the treatment of heart failure, specifically for improving symptoms and reducing the risk of hospitalization due to worsening heart failure. It can be used in patients with left ventricular dysfunction, either alone or in combination with other heart failure medications.
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): Coreg is approved for the management of hypertension to lower blood pressure. It can be used as monotherapy or in combination with other antihypertensive medications.
- Left Ventricular Dysfunction Post-Myocardial Infarction: Coreg is indicated for reducing the risk of death and future cardiovascular events in patients who have had a heart attack and have impaired function of the left ventricle.
How does Coreg work for Cardiovascular Conditions?
Coreg works by blocking certain receptors in the body known as beta-adrenergic receptors. These receptors are found in various tissues, including the heart and blood vessels. By blocking these receptors, Coreg exerts its effects on the cardiovascular system.
Here's how Coreg works for different cardiovascular conditions:
- Heart Failure: Coreg helps improve heart failure symptoms and outcomes by multiple mechanisms. It blocks beta-1 adrenergic receptors in the heart, reducing the effects of stress hormones like adrenaline. This leads to a decrease in heart rate, a reduction in the force of heart contractions, and decreased oxygen demand by the heart muscle.
- Coreg also blocks alpha-1 adrenergic receptors in blood vessels, resulting in vasodilation (widening of blood vessels) and reduced peripheral resistance. These combined actions help improve heart function and reduce the workload on the heart.
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): Coreg reduces blood pressure by blocking beta-1 adrenergic receptors in the heart, which lowers the heart rate and reduces the force of contraction. Moreover, it blocks alpha-1 adrenergic receptors in the blood vessels, causing vasodilation and resulting in decreased peripheral resistance. These effects lead to a decrease in blood pressure.
- Left Ventricular Dysfunction Post-Myocardial Infarction: Coreg helps improve outcomes in patients who have had a heart attack and have impaired left ventricular function. It blocks beta-adrenergic receptors in the heart, reducing the stress on the damaged heart muscle. This can help prevent further damage, improve heart function, and reduce the risk of future cardiovascular events.
What is Carvedilol?
Carvedilol is a medication commonly known by its brand name Coreg. It belongs to a class of drugs called beta-blockers. Carvedilol is primarily used to treat various cardiovascular conditions, including heart failure, hypertension (high blood pressure), and certain types of heart rhythm disorders.
What conditions is Carvedilol approved to treat?
Like Coreg, Carvedilol is also approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat heart failure, hypertension (high blood pressure), and left ventricular dysfunction post-myocardial infraction.
How does Carvedilol work for Cardiovascular Conditions?
As a beta-blocker, carvedilol works by blocking the effects of stress hormones, such as adrenaline, on the heart and blood vessels. It blocks certain receptors, known as beta-adrenergic receptors, helps to reduce heart rate, lower blood pressure, and improve heart function.
Carvedilol has both non-selective beta-blocking activity (affects both beta-1 and beta-2 receptors) as well as alpha-1-blocking activity. This means it not only affects the heart but also has an impact on blood vessels by causing vasodilation, which leads to a decrease in peripheral resistance and improved blood flow.
Effectiveness
How effective are Coreg and Carvedilol for treating Cardiovascular Conditions?
Coreg and Carvedilol, being the same medication, are effective for treating various cardiovascular conditions. Here are examples of studies demonstrating their effectiveness:
1. Heart Failure:
The COMET trial (Carvedilol or Metoprolol European Trial) compared Carvedilol with another beta-blocker, metoprolol, in patients with heart failure. The study found that Carvedilol reduced the risk of death and hospitalization and improved symptoms compared to metoprolol.
The COPERNICUS trial (Carvedilol Prospective Randomized Cumulative Survival) showed that Carvedilol significantly reduced the risk of death or hospitalization in patients with severe heart failure compared to placebo.
2. Hypertension (High Blood Pressure):
In a meta-analysis published in the Journal of Hypertension, Carvedilol was found to be effective in lowering blood pressure. The study concluded that Carvedilol demonstrated similar antihypertensive efficacy compared to other commonly used antihypertensive agents.
The CAPRICORN trial (Carvedilol Post-Infarct Survival Control in LV Dysfunction) showed that Carvedilol reduced the risk of death and hospitalization in patients with left ventricular dysfunction following a heart attack.
3. Left Ventricular Dysfunction Post-Myocardial Infarction:
The CAPRICORN trial mentioned above demonstrated the efficacy of Carvedilol in reducing mortality and cardiovascular events in patients with left ventricular dysfunction post-myocardial infarction.
Dosage Information
How is Coreg administered for Cardiovascular Conditions
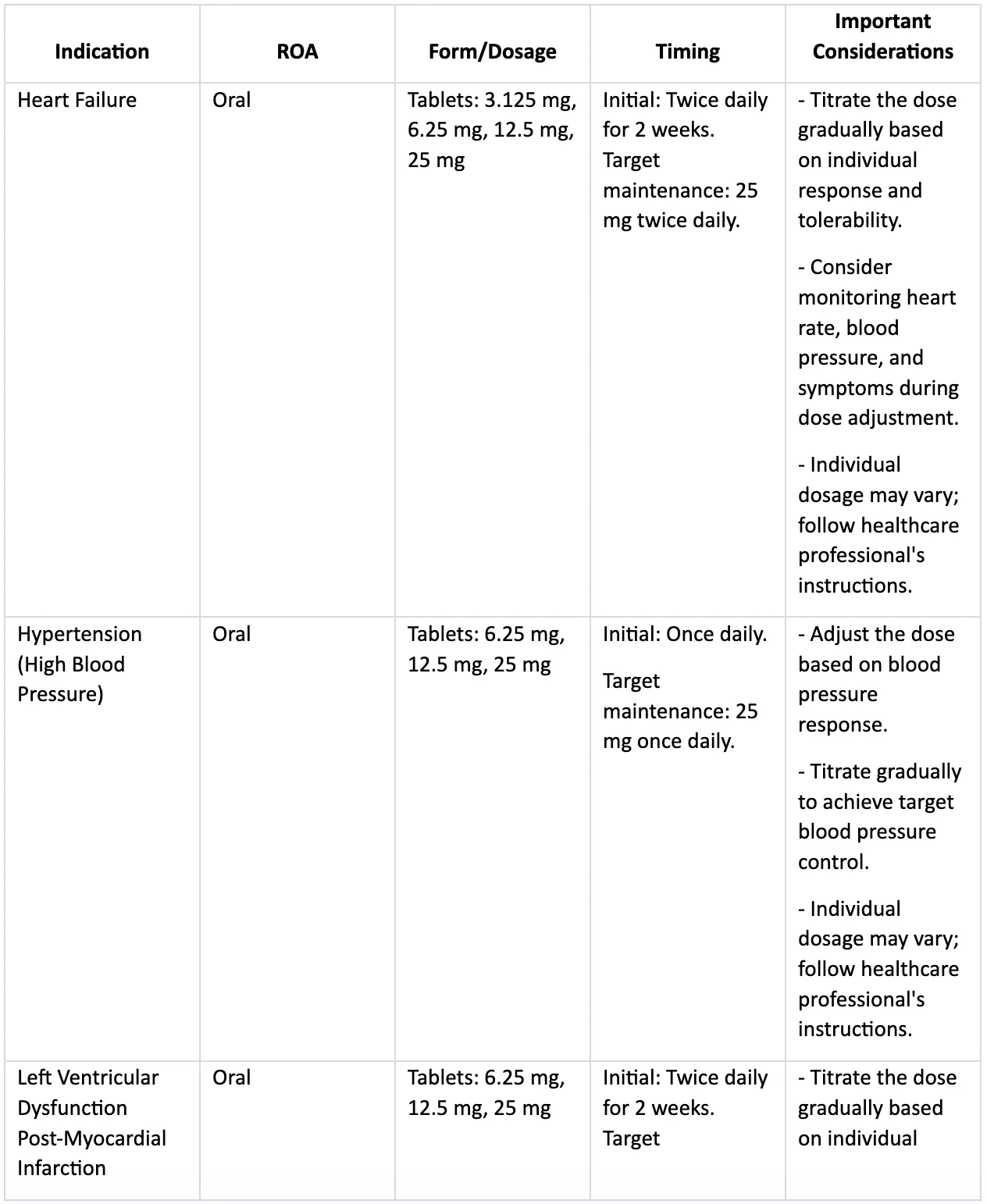
Coreg dosage information
Coreg is typically administered orally for the treatment of cardiovascular conditions. The dosage of Coreg can vary depending on the specific condition being treated and individual patient factors.
1. Heart Failure
Initial Dose: The recommended starting dose for heart failure is typically 3.125 mg twice daily for two weeks. The dose may be adjusted based on individual response and tolerability.
Target Maintenance Dose: The target maintenance dose for heart failure is usually 25 mg twice daily. However, some patients may require lower or higher doses, depending on their response and tolerance.
Titration: The dose of Coreg is often gradually increased over several weeks or months to reach the target maintenance dose. The rate of dose titration is determined by the healthcare professional based on the patient's condition.
2. Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
Initial Dose: The initial recommended dose for hypertension is typically 6.25 mg or 12.5 mg once daily. The dose may be adjusted based on blood pressure response.
Target Maintenance Dose: The target maintenance dose for hypertension is usually 25 mg once daily. However, lower or higher doses may be needed for individual patients.
Titration: Similar to heart failure, the dose of Coreg for hypertension may be adjusted gradually based on the patient's blood pressure response.
3. Left Ventricular Dysfunction Post-Myocardial Infarction
Initial Dose: The recommended starting dose for left ventricular dysfunction post-myocardial infarction is typically 6.25 mg twice daily for two weeks. The dose may be adjusted based on individual response and tolerability.
Target Maintenance Dose: The target maintenance dose for this condition is usually 25 mg twice daily. However, the dose may be adjusted based on the patient's specific needs.

How is Carvedilol Administered for Cardiovascular Conditions?
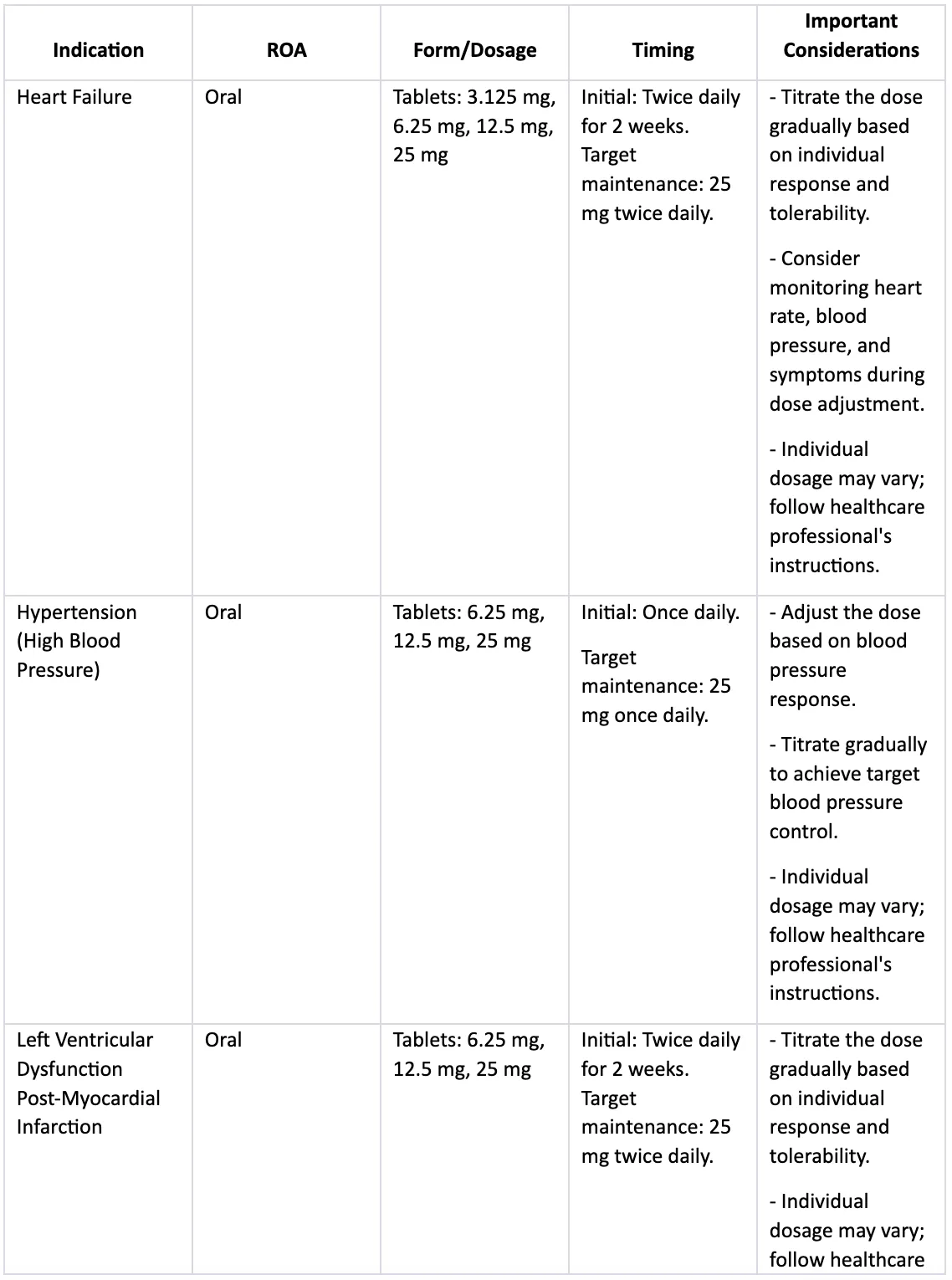
Carvedilol Dosage Information
Carvedilol, commonly known by its brand name Coreg, is administered orally for the treatment of cardiovascular conditions. It is available in tablet form and is typically taken by mouth with or without food. The specific dosage and dosing frequency depend on the condition being treated and individual patient factors.
For heart failure, the initial dose of Carvedilol is usually 3.125 mg, taken orally twice daily for the first two weeks. This starting dose helps the body adjust to the medication. Subsequently, the dose may be gradually increased to reach a target maintenance dose, which is typically 25 mg twice daily. However, the actual dosage may vary based on individual response and tolerability. It's important to follow the healthcare professional's instructions for dose adjustments and titration.
In the case of hypertension (high blood pressure), the initial dose of Carvedilol is often 6.25 mg or 12.5 mg taken once daily. The dosage may be adjusted based on the patient's blood pressure response. The target maintenance dose for hypertension is typically 25 mg once daily. Similar to heart failure, the dose may be adjusted gradually to achieve optimal blood pressure control.
For patients with left ventricular dysfunction post-myocardial infarction, the initial dose of Carvedilol is usually 6.25 mg, taken orally twice daily for the first two weeks. The dose may then be titrated up to a target maintenance dose of 25 mg twice daily. The specific dosage may vary based on individual patient characteristics and response to treatment.

Side Effects
What are the most-common side effects of Coreg?
- Fatigue: Some individuals may experience feelings of tiredness or lack of energy while taking Coreg.
- Hypotension (low blood pressure): Coreg can cause a decrease in blood pressure, leading to symptoms like dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting.
- Slow heart rate (bradycardia): Coreg may lower heart rate, resulting in a slower-than-normal heartbeat.
- Dizziness: Dizziness or lightheadedness can occur as a side effect of Coreg.
- Diarrhea: Some people may experience loose stools or diarrhea while taking Coreg.
- Weight gain: Coreg has been associated with weight gain, although the exact mechanism is not fully understood.
- Edema: Fluid retention or swelling, particularly in the lower extremities, may occur with Coreg use.
- Increased blood sugar levels: Coreg can affect blood sugar control, leading to elevated blood glucose levels in some individuals.
- Sleep disturbances: Coreg may cause sleep-related side effects, such as insomnia or vivid dreams.
- Bronchospasm: In individuals with a history of asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), Coreg can potentially cause or worsen bronchospasm, leading to difficulty breathing.
Are there any potential serious side effects of Coreg?
*If you experience these side effects, seek medical help immediately:
- Bradycardia and Heart Block: Coreg can slow down the heart rate, potentially leading to bradycardia (abnormally slow heartbeat) or heart block (interruption in the electrical signals of the heart). This can cause symptoms such as dizziness, fainting, or shortness of breath. It is important to monitor heart rate and seek medical attention if any concerning symptoms occur.
- Hypotension (Severe Low Blood Pressure): Coreg can cause a significant drop in blood pressure, leading to hypotension. Symptoms may include dizziness, lightheadedness, fainting, or feeling weak. Blood pressure should be regularly monitored, and individuals experiencing severe symptoms should seek medical assistance.
- Worsening Heart Failure: In some cases, Coreg may initially worsen heart failure symptoms, especially during the initiation or dosage adjustment period. This can include increased shortness of breath, swelling in the extremities, or rapid weight gain. Close monitoring and adjustment of medication dosages by a healthcare professional are necessary to minimize this risk.
- Bronchospasm: Coreg can potentially trigger or worsen bronchospasm in individuals with a history of asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). This can cause difficulty breathing, wheezing, or chest tightness. It is important to use Coreg with caution in individuals with respiratory conditions and to seek medical advice if any respiratory symptoms worsen.
- Liver Function Abnormalities: Rarely, Coreg may lead to liver function abnormalities, such as elevated liver enzymes or hepatitis. Signs of liver problems can include yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice), dark urine, persistent nausea or vomiting, or abdominal pain. If any of these symptoms occur, medical attention should be sought promptly.
What are the most-common side effects of Carvedilol?
- Headache: Carvedilol can occasionally cause headaches in some individuals.
- Nausea: Some people may experience feelings of nausea or an upset stomach while taking Carvedilol.
- Dry eyes: Carvedilol may lead to dryness or discomfort in the eyes.
- Skin reactions: Rarely, Carvedilol can cause skin reactions such as rash, itching, or hives.
- Muscle weakness: In some cases, Carvedilol may result in muscle weakness or fatigue.
- Insomnia: Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep may occur as a side effect of Carvedilol.
- Mood changes: Carvedilol might rarely lead to mood changes or depression in certain individuals.
- Blurred vision: Carvedilol can cause temporary blurred vision or changes in vision clarity.
- Increased triglyceride levels: In some cases, Carvedilol may cause an elevation in blood triglyceride levels.
- Joint pain: Joint pain or discomfort has been reported as a potential side effect of Carvedilol.
Are there any potential serious side effects of Carvedilol?
*If you experience these side effects, seek medical help immediately:
- Allergic reactions: In rare cases, Carvedilol can trigger serious allergic reactions. Symptoms may include difficulty breathing, chest tightness, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, and hives. Seek emergency medical assistance if you experience signs of an allergic reaction.
- Respiratory difficulties: In individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions, Carvedilol can cause or exacerbate bronchospasm or difficulty breathing. This may occur in people with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Seek medical advice if respiratory symptoms worsen.
- Hepatic dysfunction: Rarely, Carvedilol may cause liver function abnormalities, including elevated liver enzymes or hepatitis. Symptoms may include yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice), dark urine, persistent nausea or vomiting, or abdominal pain. Immediate medical attention is necessary if these signs occur.
Contraindications and Interactions
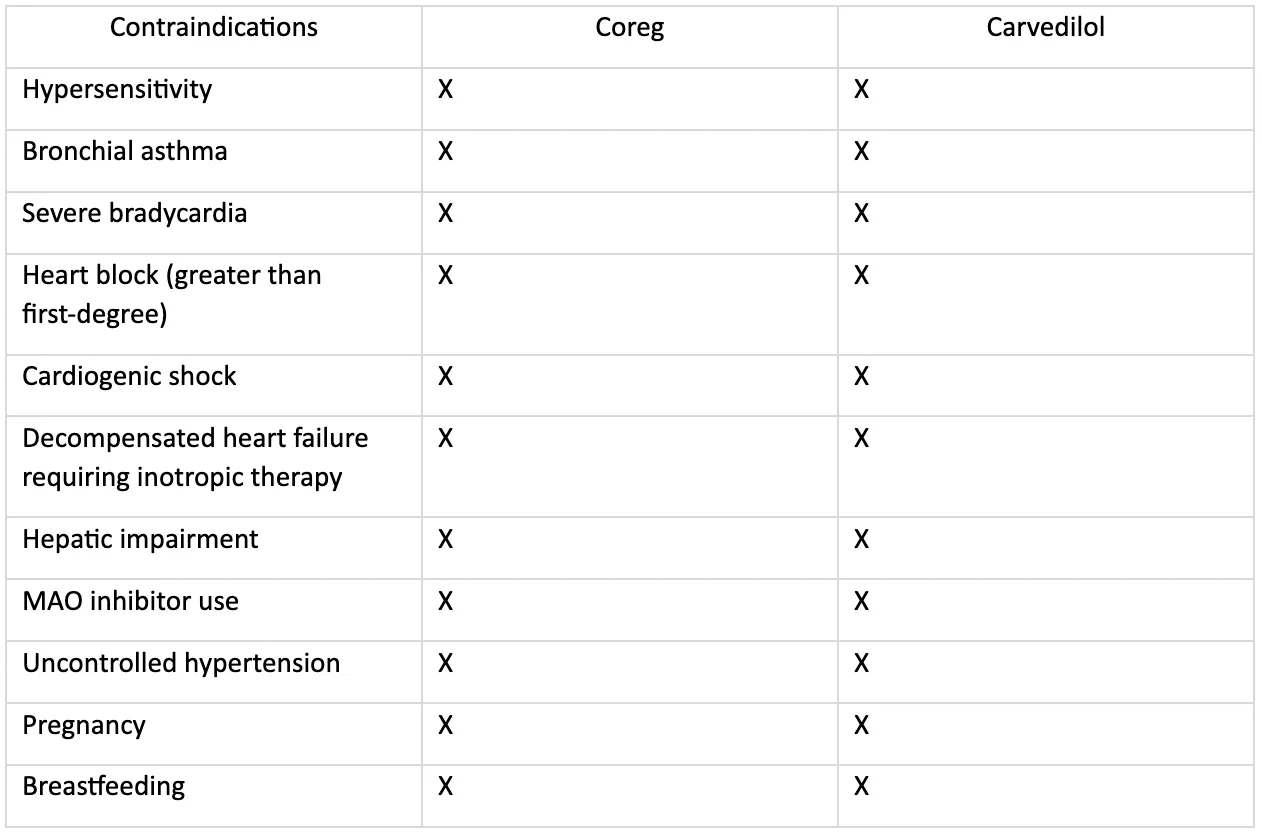
Warnings and General Precautions for Coreg and Carvedilol
Coreg and Carvedilol share similar warnings and general precautions due to their active ingredient. These include:
- Asthma and respiratory conditions: Both medications should be used with caution in individuals with a history of asthma or other respiratory conditions. Carvedilol can potentially cause or worsen bronchospasm, leading to breathing difficulties. Close monitoring of respiratory function is necessary, and alternative treatment options may be considered in severe cases.
- Diabetes and blood sugar control: Coreg and Carvedilol can affect blood sugar levels and may mask certain symptoms of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Individuals with diabetes should carefully monitor their blood sugar levels while taking these medications, and adjustments to diabetes management plans may be necessary.
- Peripheral vascular disease and Raynaud's phenomenon: Carvedilol may exacerbate symptoms in individuals with peripheral vascular disease or Raynaud's phenomenon, which involves decreased blood flow to the extremities. Close monitoring and adjustment of treatment may be required to prevent worsening of symptoms.
- Hepatic impairment: Both medications should be used with caution in individuals with liver disease or impaired liver function. Carvedilol is metabolized by the liver, and dosage adjustments may be necessary to avoid potential complications.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Coreg and Carvedilol are generally not recommended for use during pregnancy or breastfeeding unless the potential benefits outweigh the risks. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to evaluate the risks and determine the best course of action.
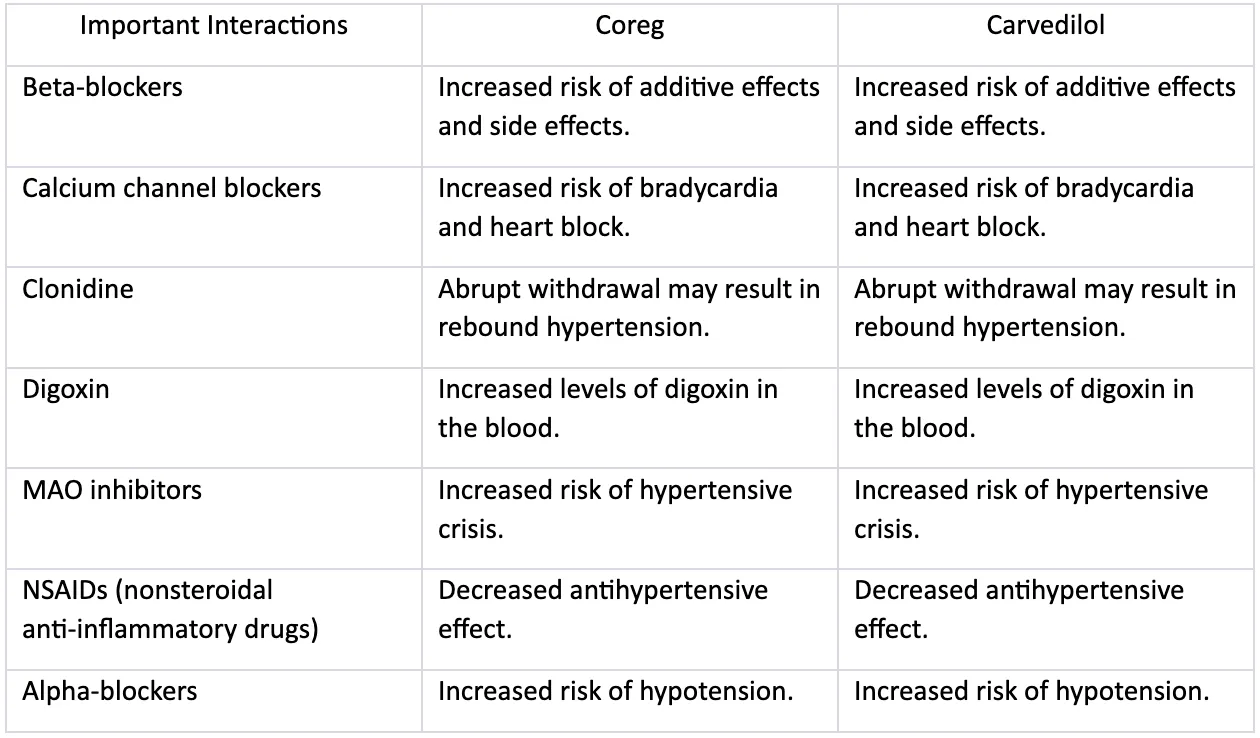
Contraindications and Important Interactions for Coreg and Carvedilol

Cost Comparision
How much do Coreg and Carvedilol cost?
Based on the pharmacy you visit, you will find that an oral tablet of Coreg (3.125 mg) costs approximately $761. This is the price for 100 tablets.
Similarly, 100 oral tablets of Carvedilol (25 mg) cost approximately $19.
Popularity of Coreg and Carvedilol
Coreg and Carvedilol rank as the 29th most popular drug in the U.S., according to 2020 statistics. It is estimated that 4,948,170 patients in the U.S. use these drugs.
Conclusion
Takeaway
In conclusion, Coreg and Carvedilol are medications that share the same active ingredient and are commonly used in the treatment of cardiovascular conditions. They are both beta-blockers that work by blocking certain receptors in the body, resulting in various cardiovascular effects. While Coreg is a brand-name medication, Carvedilol is the generic version.
Both Coreg and Carvedilol have shown effectiveness in managing conditions such as heart failure and hypertension. Clinical studies have demonstrated their ability to improve symptoms, reduce hospitalizations, and enhance overall cardiac function. However, the choice between Coreg and Carvedilol may depend on factors such as individual patient characteristics, tolerability, cost, and healthcare provider preference.
It is important to note that Coreg and Carvedilol can have common side effects such as fatigue, dizziness, and low blood pressure. Additionally, they may have serious side effects that require close monitoring and medical attention.
Considering their similarities in efficacy, safety profiles, and mode of action, the decision between Coreg and Carvedilol may involve factors such as availability, cost, insurance coverage, and individual patient response. Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in assessing patients' needs, considering potential interactions, and tailoring treatment plans to optimize outcomes.
Ultimately, the choice between Coreg and Carvedilol should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional who can provide personalized recommendations based on the specific cardiovascular condition, medical history, and individual needs of the patient.