Eplerenone vs Spironolactone
Introduction
Hypertension is a medical term for higher than recommended blood pressure. According to the health institution such as the American College of Cardiology (ACC), blood pressure (BP) is measured according to the following guidelines:
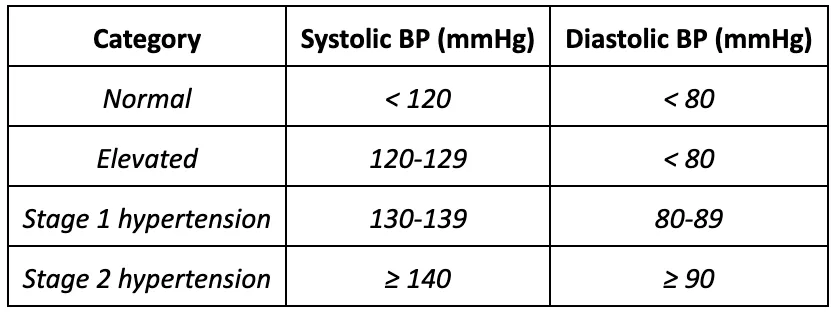
As of 2020, Stage 1 and Stage 2 hypertension affects an estimated 48% of the adult population in the US, which comes to approximately 119 million. Moreover, it is a condition that increases the risks of heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes, which, in the country, are the leading causes of death.
Eplerenone and spironolactone are two medications used to treat hypertension in adults. While eplerenone is derived from spironolactone, they have different chemical compositions, which results in varying side effects and contraindications.
Note that neither of these medications cures hypertension. Rather they are to be used with other therapies to control blood pressure to keep it in the recommended range.
About eplerenone and spironolactone
What is eplerenone?
Eplerenone is a generic drug classified as a selective aldosterone receptor antagonist and potassium-sparing diuretic that was patented in 1983 and FDA-approved in 2002.
Chemically known as 9,11α-epoxy-7α-methoxycarbonyl-3-oxo-17α-pregn-4-ene-21,17-carbolactone, eplerenone is derived from spironolactone but replaces the 17α-thioacetyl group of spironolactone with a carbomethoxy group and introduces a 9α,11α-epoxy bridge.
As a selective aldosterone receptor antagonist, eplerenone blocks the effects of the hormone aldosterone, produced by the adrenal glands. However, these drugs also increase the amount of potassium ions excreted during urination, which can cause potassium in the body to fall below safe levels, a condition known as hypokalemia. So, by also being a potassium-sparing diuretic, eplerenone counters this effect and prevents the excessive loss of potassium ions.
What conditions is eplerenone approved to treat?
Eplerenone is FDA-approved to treat hypertension, particularly resistant hypertension, alone or co-administered with other treatments and heart failure in post-myocardial infarction (MI) patients.
How does eplerenone work for hypertension?
Eplerenone treats hypertension by blocking the effects of aldosterone. This hormone increases sodium reabsorption in the salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon to encourage water loss. By blocking this reabsorption, it decreases the amount of water lost by the body, which in turn it decreases blood pressure in vessels. https://www.drugs.com/drug-class/aldosterone-receptor-antagonists.html
What is spironolactone?
Spironolactone is an aldosterone receptor antagonist, but not as selective as eplerenone, and a potassium-sparing diuretic discovered in 1959 and FDA approved in 1960.
Its chemical formula is 7α-Acetylthio-17α-hydroxy-3-oxopregn-4-ene-21-carboxylic acid γ-lactone, and it blocks the effects of aldosterone comparatively more extensively than eplerenone.
What conditions is spironolactone approved to treat?
Spironolactone is FDA-approved to treat the following health conditions:
- Add-on therapy for hypertension
- Heart failure (NYHA class III-IV)
- Reduced ejection fraction
- Managing edema
- Short-term preoperative treatment for primary hyperaldosteronism
- Long-term maintenance for primary hyperaldosteronism in patients with:
- Discrete aldosterone-producing adrenal adenomas that are not candidates for surgery
- With bilateral macronodular or micro adrenal hyperplasia
How does spironolactone work for hypertension?
Like eplerenone, spironolactone blocks the effects of aldosterone to reduce sodium reabsorption and water loss, which decreases blood pressure. Additionally, it stops the excess excretion of potassium ions to prevent hypokalemia.
Effectiveness
How effective are eplerenone and spironolactone for treating hypertension?
Both eplerenone and spironolactone have been shown to be effective treatments for resistant hypertension, as shown by the findings of numerous clinical trials over the years.
The EPHESUS study conducted in 2003 showed that for patients who suffered left ventricular dysfunction and acute heart failure after an acute myocardial infarction, eplerenone was an effective therapy for reducing blood pressure.
Additionally, in a randomized aldosterone antagonism trial conducted in 2011, eplerenone was shown to be more effective at reducing blood pressure in patients when compared to a placebo.
Considering spironolactone, the landmark Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study (RALES) trial conducted in 1995 showed the therapeutic effects of spironolactone given to patients with severe heart failure and found it significantly reduced hypertensive measurements for a majority of patients compared to a placebo. This result was further verified in a systematic review of five monotherapy trials over the years.
Moreover, all these trials for eplerenone and spironolactone confirmed that both these drugs had maximum effective dosages of approximately 100 mg. More than this amount and blood pressure did not reduce further.
Furthermore, spironolactone was shown to be more effective than eplerenone, with certain studies suggesting that 50 mg of eplerenone was equivalent to the effects of 25 mg of spironolactone.
Dosage information
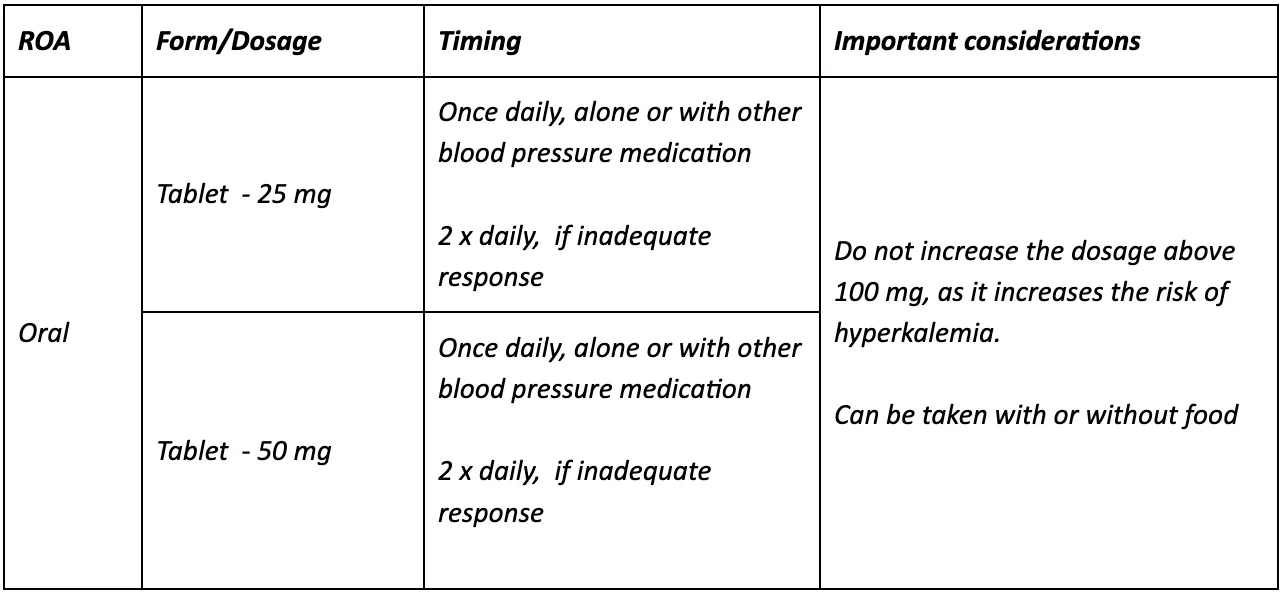
How is eplerenone administered for hypertension?
Eplerenone is an additional therapy for controlling hypertension and is available as a film-coated tablet taken orally without chewing. This tablet can be taken on an empty stomach or with food, although it is advised to take after eating as it reduces the chances of an upset stomach.
Additionally, taking eplerenone early in the day is recommended as this medication increases urination, which can be bothersome at night.
If patients have difficulty swallowing the tablet, it can be crusted and misted into a tablespoon of applesauce or yogurt and must be consumed immediately.
When patients begin eplerenone, dosages start at 25 mg daily and monitor response. If blood pressure has not decreased and potassium levels are still acceptable, dosages are increased to 50 mg. However, dosages do not exceed 100 mg because studies have found that above 100 mg of eplerenone increases the risk of hyperkalemia.
Eplerenone dosage information
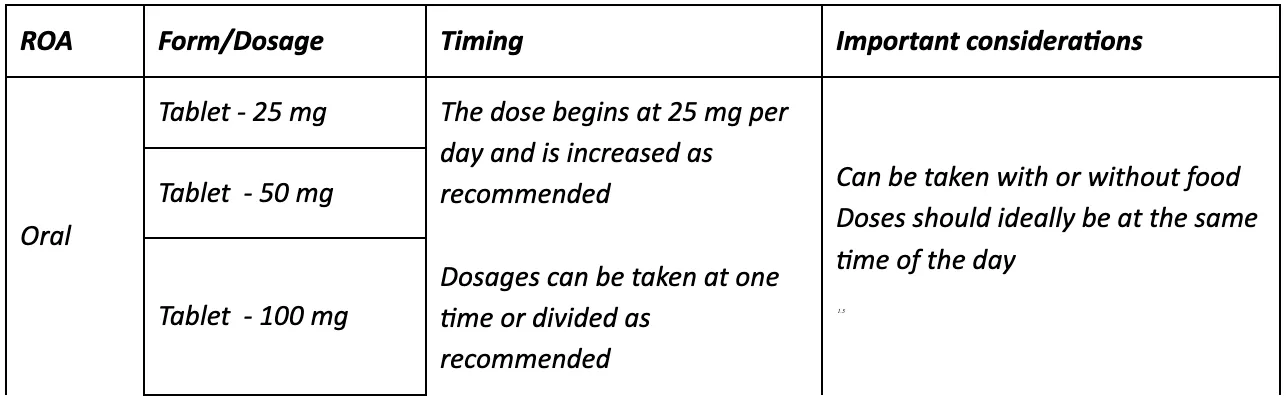
How is spironolactone administered for hypertension?
For hypertension, spironolactone is an add-on therapy. It is available in three dosages ( 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg) and can be taken with food or without.
Initial treatment begins at 25 mg and can be increased up to 100 mg every two weeks depending on the response and potassium levels. However, dosages must not exceed 100 mg as it increases the risk of hyperkalemia without substantially reducing blood pressure.
If a dose is missed, patients need to take their dose of spironolactone as soon as they remember. However, if the next scheduled dose is too close, they should skip it. Double dosing is not recommended.
Spironolactone dosage information
Side Effects
What are the most common side effects of eplerenone?
The most common side effects seen among patients taking eplerenone include:
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Higher potassium levels
Are there any potential serious side effects of eplerenone?
There are a few potential serious side effects of eplerenone. If patients experience any of the following, they should contact a healthcare provider immediately:
- Excessive diarrhea
- Unexplained vomiting
- Fast, irregular heartbeat
- Little or no urination
- Difficulty breathing
- Swelling in lower limbs
- Symptoms of hyperkalemia include:
- Constant nausea
- Weakness
- Tingling feelings in various areas of the body
- Irregular heartbeat
- Chest pains
- Loss of movement
- Constant headaches
What are the most common side effects of spironolactone?
The most common side effects seen among patients taking spironolactone include:
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Breast tenderness and swelling in both males and females
- Diarrhea
- Upset stomach
- Vomiting
- Higher potassium levels
Are there any potential serious side effects of spironolactone?
There are a few potential serious side effects of spironolactone. If patients experience any of the following, they should contact a healthcare provider immediately:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding or changes to the menstrual cycle
- Enlarged or painful breasts
- Sexual dysfunction
- Excessive nausea
- Unexplained vomiting
- Vomit that resembles coffee grounds
- Severe stomach or abdominal pain
- Little or no urination
- Dark urination
- Fatigue or weakness
- Muscle spasms
- Emotional changes or mood swings
- Unexplained signs of infections
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes
- Easy bleeding or bruising
- Symptoms of hyperkalemia, including:
- Constant nausea
- Weakness
- Tingling feelings in various areas of the body
- Irregular heartbeat
- Chest pains
- Loss of movement
Contraindications and interactions
Warnings and general precautions for eplerenone and spironolactone
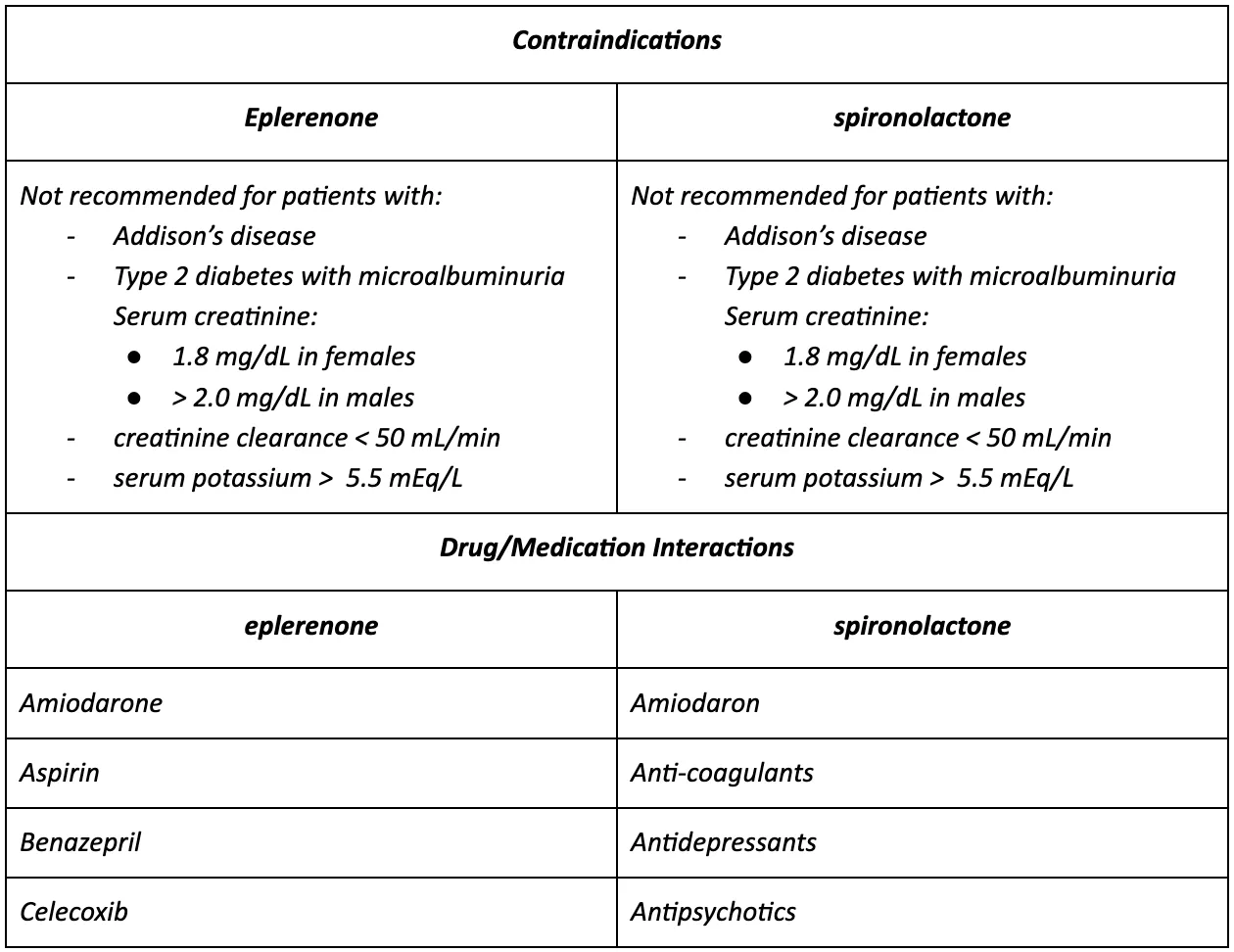
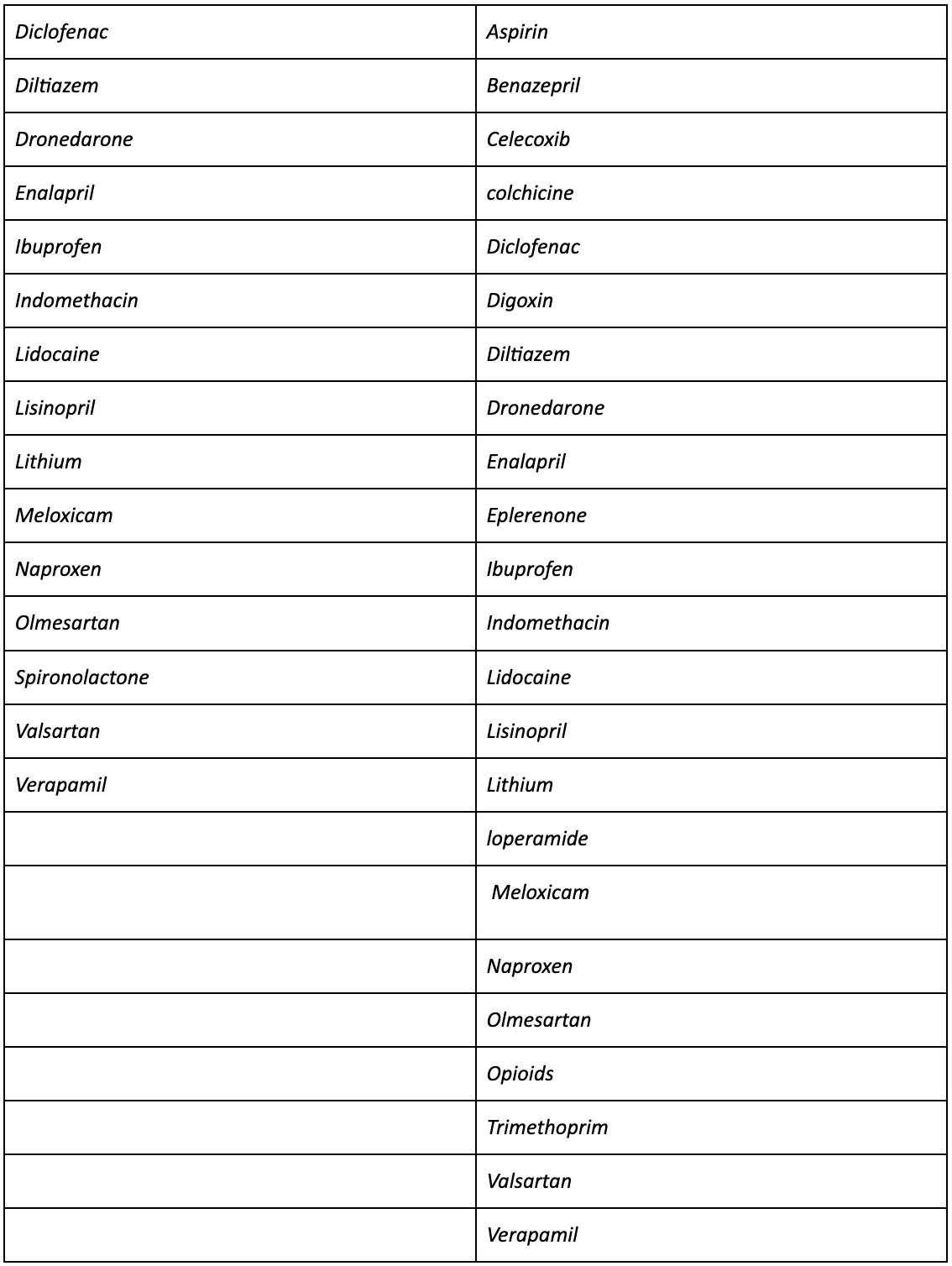
As eplerenone is derived from spironolactone, both have similar contraindications. Both medications are not advised for patients with kidney problems, impaired liver function, and untreated salt imbalances in the body, such as higher-than-normal levels of potassium or lower-than-normal levels of salt. Therefore, it is contraindicated in all patients with:
- serum potassium > 5.5 mEq/L
- creatinine clearance ≤ 30 mL/min
Additionally, neither medication is recommended for patients with:
- Decreases adrenal gland function, such as Addison’s disease
- Type 2 diabetes with microalbuminuria,
- serum creatinine > 1.8 mg/dL in females or > 2.0 mg/dL in males
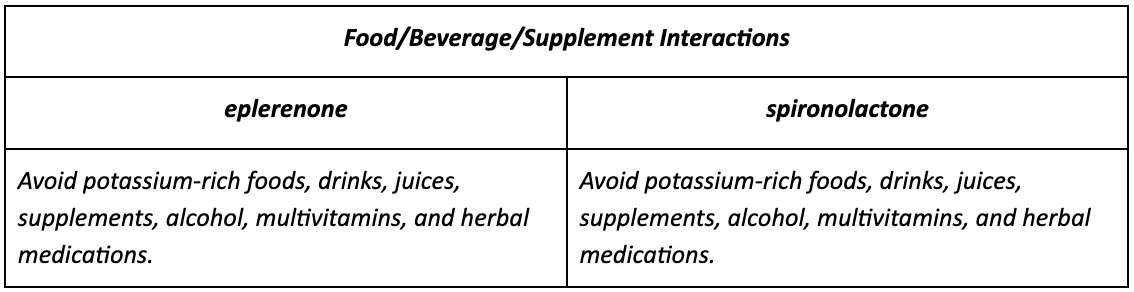
Moreover, both these medications are potassium-sparing, which means they will increase potassium levels. Therefore patients must avoid foods, salt substitutes, and mineral supplements high in potassium.
Currently, there are no conclusive findings that determine the effects of either eplerenone or spironolactone in pregnant women. Still, it is recommended to use either medication with caution during pregnancy and only when needed. Furthermore, both drugs can pass into breast milk, but animal studies suggest it is unlikely to harm a nursing infant. However, a healthcare professional should be consulted to determine if either medication is advisable or can be substituted with safer options.
Contraindications and important interactions for eplerenone and spironolactone
Cost Comparison
How much do eplerenone and spironolactone cost?
30 tablets of 25 mg eplerenone range from $25.45 - $27.95, for an average cost of $0.89 per tablet. Therefore a patient taking a dosage of 50 mg per day averages $1.78/day.
30 tablets of 25 mg spironolactone range from $8.64 - $13.25, for an average of $0.73 per tablet. Therefore a patient taking a dosage of 50 mg per day averages $1.46/day.
Popularity of eplerenone and spironolactone
Given its FDA approval in 1960, spironolactone use is more prevalent, with over 13 million prescriptions filled in 2020, making it the 51st most prescribed drug in the US. Eplerenone is still not widely used and, as of 2020, does not rank in the top 300 prescription medications in the country. However, neither drug is a first-line treatment for high blood pressure, which is why both are ranked lower than other antihypertensive medications.
Conclusion
Takeaway
Both eplerenone and spironolactone are effective medications for treating hypertension, but the efficacy of spironolactone is much better, so spironolactone is prescribed more often. Additionally, it costs comparatively less, making it the more economical choice for hypertension patients.
However, both medications can increase the risk of hyperkalemia, so any patient taking either must follow a diet low in potassium. Finally, both eplerenone and spironolactone are add-on therapies. Patients need to overhaul their lifestyles to include healthy changes and use additional therapies to ensure their hypertensive condition is under control.