Fenofibrate vs Lipitor
Introduction
Healthcare professionals often rely on medication to help patients achieve optimal lipid profiles when managing high cholesterol levels. Two commonly prescribed drugs are fenofibrate and Lipitor (generic name: atorvastatin). While both medications target cholesterol, they belong to different drug classes and work through distinct mechanisms.
Fenofibrate acts by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-alpha), a nuclear receptor involved in lipid metabolism. On the other hand, Lipitor functions by inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which plays a vital role in cholesterol synthesis.
This article will examine the main differences between Fenofibrate and Lipitor, including their purpose, mechanism of action, dosage, side effects, contraindications and side effects, costs, popularity, and more. Continue reading to learn more about Fenofibrate and Lipitor.
What is Fenofibrate?
Fenofibrate belongs to the fibrates class of drugs. Fenofibrate is available in the market under ten different brand names and is primarily used to treat high levels of triglycerides (fat) in the blood, along with certain abnormal cholesterol levels. Fenofibrate works by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-alpha), a nuclear receptor involved in lipid metabolism.[1]
What conditions are Fenofibrate approved to treat?
Fenofibrate is approved by the FDA for the treatment of the following conditions:[2]
- Hypertriglyceridemia:
Fenofibrate is primarily used to treat high levels of triglycerides in the blood, a condition known as hypertriglyceridemia. Elevated triglyceride levels are often associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. Fenofibrate helps lower triglyceride levels by reducing their production in the liver and enhancing their breakdown.[3]
- Mixed Dyslipidemia:
Fenofibrate is also approved for the treatment of mixed dyslipidemia. This condition refers to the presence of abnormal levels of both triglycerides and cholesterol in the blood. Fenofibrate can help improve the lipid profile by reducing triglyceride levels and modestly lowering low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol while increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol.[4]
How does Fenofibrate work for high cholesterol?
Fenofibrate primarily acts on high cholesterol levels by modulating lipid metabolism through its mechanism of action. Fenofibrate belongs to a class of drugs called fibrates, and its main mechanism of action involves activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-alpha), a nuclear receptor found in various tissues, including the liver.[5] PPAR-alpha plays a crucial role in regulating lipid metabolism.
Once Fenofibrate activates PPAR-alpha, it induces the transcription of genes involved in lipid metabolism. This affects lipoproteins and enzymes responsible for cholesterol and triglyceride processing. Fenofibrate's activation of PPAR-alpha results in an increased lipolysis, which enhances the breakdown of triglycerides stored in adipose tissue.[6] The liberated fatty acids are then utilized as an energy source. Additionally, Fenofibrate reduces the liver's production of triglycerides, further contributing to the decrease in triglyceride levels.
Fenofibrate promotes the production of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, often called "good cholesterol." HDL cholesterol helps remove excess cholesterol from peripheral tissues and transports it back to the liver for excretion, thus reducing the overall cholesterol burden.[7]
What is Lipitor?
Lipitor is the brand name for the medication known as atorvastatin. It belongs to a class of drugs called statins, which are commonly prescribed for treating high cholesterol and preventing cardiovascular diseases. Lipitor is one of the most widely prescribed statin medications.[8]
What conditions is Lipitor approved to treat?
Lipitor (atorvastatin) is approved by regulatory authorities, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), for the treatment of the following conditions:[9]
- High Cholesterol (Hypercholesterolemia):
Lipitor is primarily prescribed to lower elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, commonly known as "bad cholesterol." High LDL cholesterol levels are a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes. Lipitor helps reduce LDL cholesterol levels, thereby decreasing the risk of cardiovascular events.[10]
- Dyslipidemia:
Lipitor is also indicated for treating dyslipidemia, which refers to abnormal lipid levels in the blood. This condition can involve elevated LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and decreased high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol. By targeting LDL cholesterol, Lipitor helps correct dyslipidemia and improve the overall lipid profile.[11]
- Cardiovascular Risk Reduction:
Lipitor is prescribed to reduce the risk of major cardiovascular events, including heart attacks, strokes, and the need for revascularization procedures (such as angioplasty or coronary artery bypass surgery). It is commonly used as a preventive medication in individuals with multiple risk factors for cardiovascular diseases, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or a history of cardiovascular events.[11]
How does Lipitor work for high cholesterol?
Lipitor (atorvastatin) belongs to the statins class of medication. Its mechanism of action involves inhibiting the enzyme called 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMG-CoA reductase), which plays a significant role in cholesterol synthesis in the liver.[13]
Lipitor blocks the activity of HMG-CoA reductase, the rate-limiting enzyme in the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway. Lipitor reduces the liver's ability to produce cholesterol by inhibiting this enzyme. Lipitor lowers the production of mevalonic acid, an intermediate compound in the cholesterol synthesis pathway, by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase. This, in turn, reduces the synthesis of cholesterol in the liver.
When cholesterol levels in the liver decrease due to Lipitor's action, it triggers a feedback mechanism. The liver increases the expression of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptors on its surface. LDL receptors help remove LDL cholesterol (often called "bad cholesterol") from the bloodstream by binding to LDL particles and internalizing them into liver cells for breakdown and removal. The increased expression of LDL receptors leads to enhanced clearance of LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream. This results in a reduction of LDL cholesterol levels, which is beneficial for cardiovascular health.[14]
Effectiveness
How effective are Fenofibrate and Lipitor for high cholesterol?
Fenofibrate and Lipitor (atorvastatin) are effective medications for managing lipid disorders and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases related to high cholesterol. However, their effectiveness may vary depending on the patient's specific lipid profile and individual characteristics.
Fenofibrate is highly effective in reducing triglyceride levels, particularly in individuals with elevated triglycerides or hypertriglyceridemia. It can significantly lower triglyceride levels by 20% to 50%.[15] Fenofibrate also positively affects raising high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, often referred to as "good cholesterol." It can increase HDL cholesterol levels by approximately 10% to 20%.[16]
On the other hand, Lipitor is highly effective in lowering LDL cholesterol levels, which is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. It can reduce LDL cholesterol by approximately 40% to 60%.[17] While Lipitor's primary focus is on LDL cholesterol, it can also lead to a modest reduction in triglyceride levels of around 10% to 30%.[18] Lipitor may cause a slight increase in HDL cholesterol levels, typically ranging from 5% to 15%.[19]
Dosage Information
How is Fenofibrate administered for high cholesterol?
Fenofibrate is available in the market in the form of tablets or capsules. Depending on the specific formulation, you can take Fenofibrate with or without food. However, it's important to follow the instructions provided with your medication. Some formulations may be more effective with food to enhance absorption, while others can be taken on an empty stomach.
Fenofibrate is usually taken once daily. Your healthcare professional will determine the duration of fenofibrate treatment based on your lipid profile, the underlying condition, and your response to the medication.
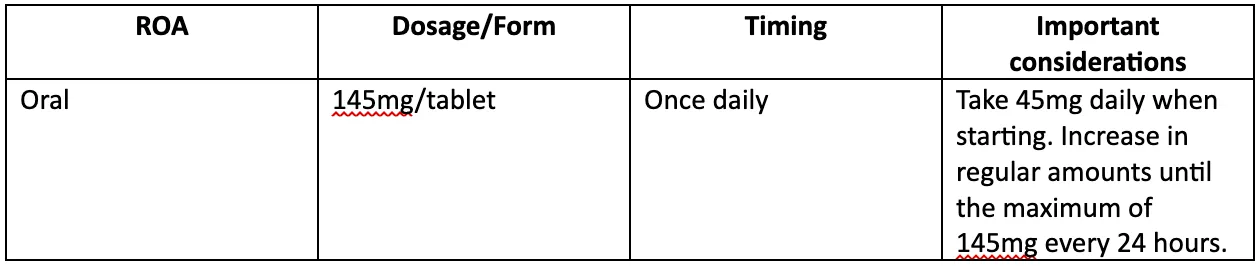
Fenofibrate dosage information
The proper dosage of Fenofibrate can vary depending on the brand name you use and the condition you have. The typical dosage range for Fenofibrate is 48 mg to 145 mg, taken orally once daily. The table below illustrates the dosage information of Fenofibrate (Tricor) based.
Table 1. Fenofibrate (Tricor) dosage information:
How is Lipitor administered for high cholesterol?
Lipitor (atorvastatin) is available in the form of oral tablets. The tablets are designed to be swallowed whole with water. Lipitor tablets' specific strengths and appearances may vary depending on the country and the manufacturer. Common strengths available include 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg, and 80 mg. Each tablet's strength is usually color-coded for easy identification, but the exact appearance may differ among brands.
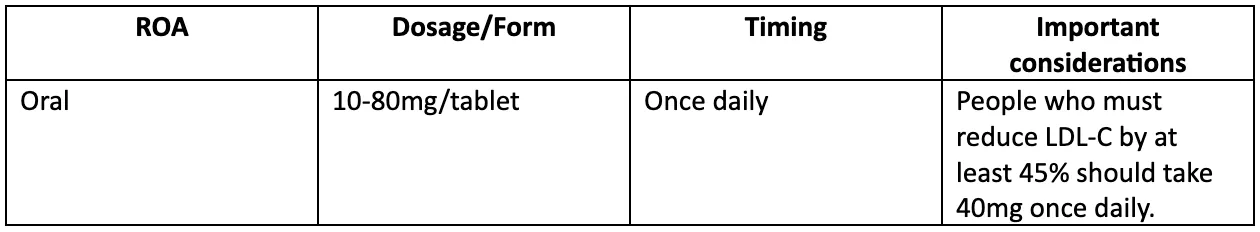
Lipitor Dosage information
The table below illustrates the dosage information for Lipitor.
Table 2. Lipitor dosage information
Side Effects
What are the most common side effects of Fenofibrate?
Common side effects of Fenofibrate include the following:
- Runny nose
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue
Are there any potentially serious side effects of Fenofibrate?
If you experience any of these serious side effects, seek medical help immediately:
- Sharp pain in the stomach
- Skin rash
- Jaundice
- Fever
- Chest pain or trouble breathing
- Pancreatitis
What are the most common side effects of Lipitor?
Some of the most common side effects of Lipitor include the following:
- Muscle or bone pain
- painful urination
- muscle spasms
- Stomach problems
- Insomnia
- runny nose
- Diarrhea and nausea
Are there any potentially serious side effects of Lipitor?
If you experience any of these serious side effects, seek medical help immediately:
- Skin rash
- Kidney failure
- Muscle weakness
- Pancreatitis
- Liver problems
- High blood sugar
Contraindications and Interactions
Warnings and general precautions for Fenofibrate and Lipitor
Warnings and general precautions for Fenofibrate and Lipitor (atorvastatin) include the following:
- If liver function tests become significantly elevated or signs of liver disease occur, treatment with Fenofibrate should be discontinued.
- If gallbladder symptoms occur, Fenofibrate should be discontinued.
- If severe abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting occurs, Fenofibrate should be discontinued, and medical attention should be sought.
- Fenofibrate and Lipitor should not be used during pregnancy or while breastfeeding, as they may cause harm to the developing fetus or nursing infant.
- Patients with a stroke or thyroid disorder history should not take the medication.
- Avoid eating food that is rich in cholesterol while on either medication.
Contraindications and important interactions for Fenofibrate and Lipitor
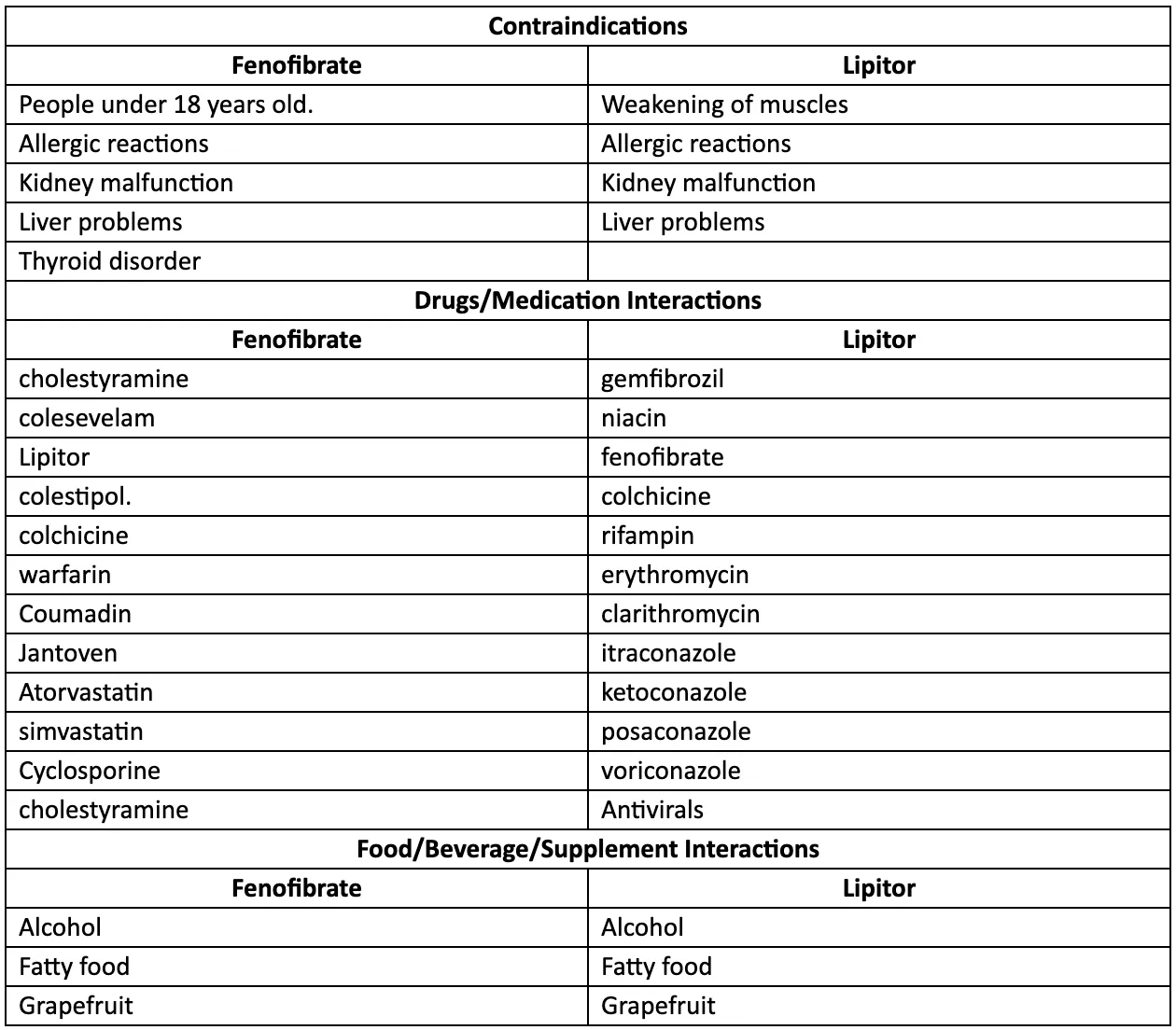
Cost Comparison
How much do Fenofibrate and Lipitor cost?
Fenofibrate is generally available in generic form, which tends to be less expensive than brand-name versions. The cost of generic Fenofibrate can range from around $10 to $50 for a one-month supply, but this can vary depending on the medication's strength.[20]
As for Lipitor, it is a brand-name medication, and the cost tends to be higher compared to generic alternatives. The price of Lipitor can range from around $500 or more for a one-month supply, depending on the dosage and quantity prescribed.[21]
Popularity of Fenofibrate and Lipitor
Fenofibrate has been available as a generic medication for several years, making it a cost-effective option for many patients. It is prescribed by healthcare professionals worldwide and has been used extensively to manage lipid disorders. According to reports, there are more than 7.5 million prescriptions in the U.S.[22]
Lipitor has gained significant popularity due to its efficacy, long-standing presence in the market, and extensive clinical research supporting its effectiveness and safety. It has been widely prescribed globally and has remained a commonly used medication for managing cholesterol levels. According to reports, there are more than 114 million prescriptions of Lipitor in the U.S.[23]
Conclusion
Takeaway
fenofibrate and Lipitor are effective medications for managing cholesterol levels but differ in their mechanisms of action and lipid profile effects. Fenofibrate primarily targets triglycerides and HDL cholesterol, making it useful for individuals with high triglyceride levels. Conversely, Lipitor is highly effective at lowering LDL cholesterol, making it a preferred choice for patients with elevated LDL levels. When considering these medications, assessing the patient's lipid profile, medical history, and potential drug interactions is crucial to determine the most appropriate choice.